Before digging into all the National Park Service (NPS) data, my first goal was to understand the organization. I wanted to learn how something becomes part of the NPS (aka a Unit) and what the different designations signify. This provided me a way of understanding what I may learn or experience at each site.
Once a location is identified as a potential unit, the below flowchart outlines the general path it takes on its journey through our legislative and executive branches. Most NPS units are established via Congress, with National Monuments also able to be proclaimed independently by the President of the United States.
How are units added to the National Park Service?
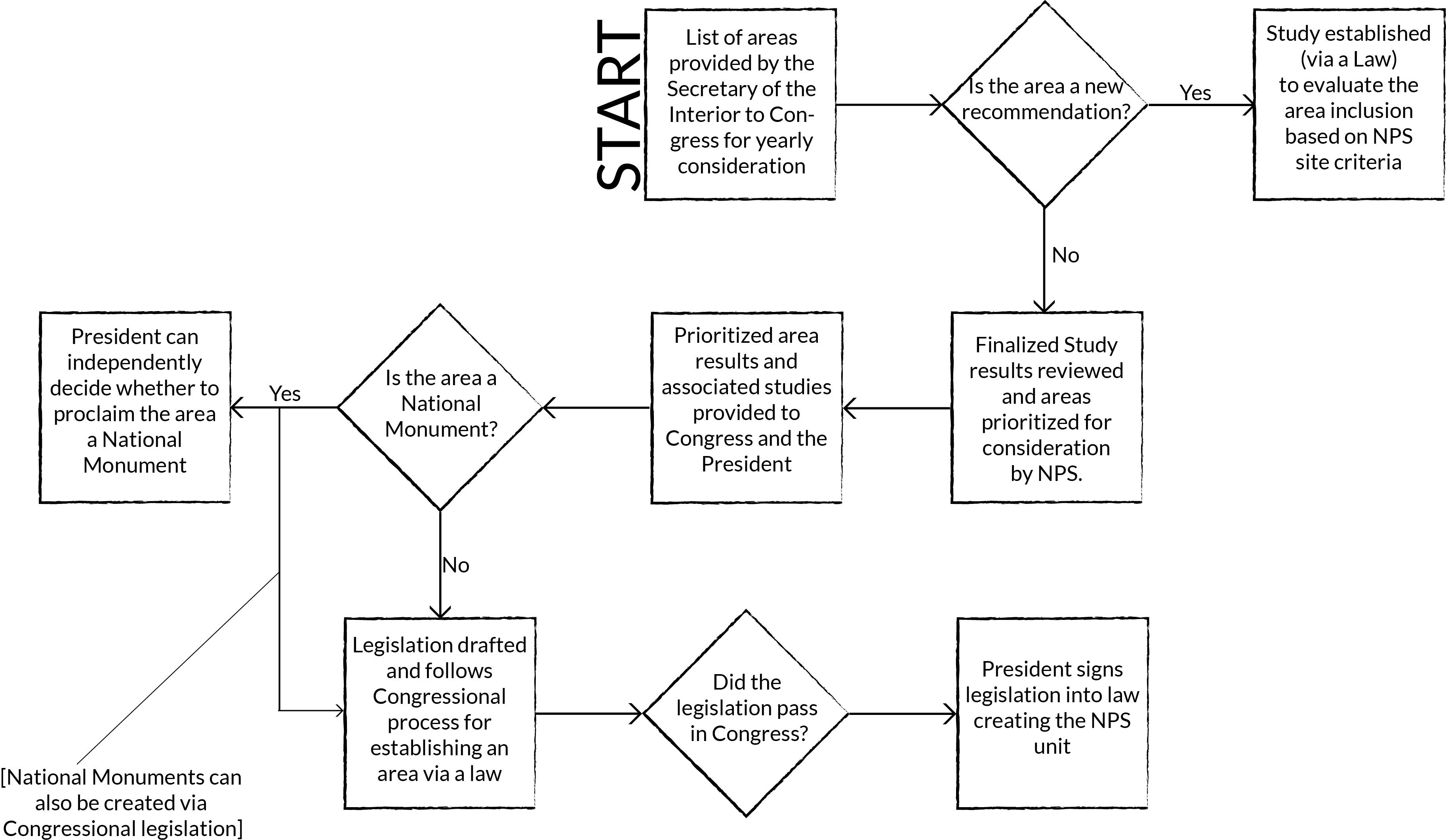
Source: Congressional Research Service: https://www.fas.org/sgp/crs/misc/RS20158.pdf
How are the National Park Service units organized and what are their characteristics?
From this I began reading about the different units within the NPS and one of my first questions was “What do all the unit designations mean? What are the differences between them?” The first thing to understand is the required criteria for any unit of the NPS. The unit must be of national importance/significance and possess all the following standards:
- Is an outstanding example of a particular type of resource
- Possesses exceptional value or quality in illustrating or interpreting the natural or cultural themes of our Nation’s heritage
- Offers superlative opportunities for recreation for public use and enjoyment, or for scientific study.
- Retains a high degree of integrity as a true, accurate, and relatively unspoiled example of the resource
There are many similarities between the unit designations. This chart illustrates the significant differences.
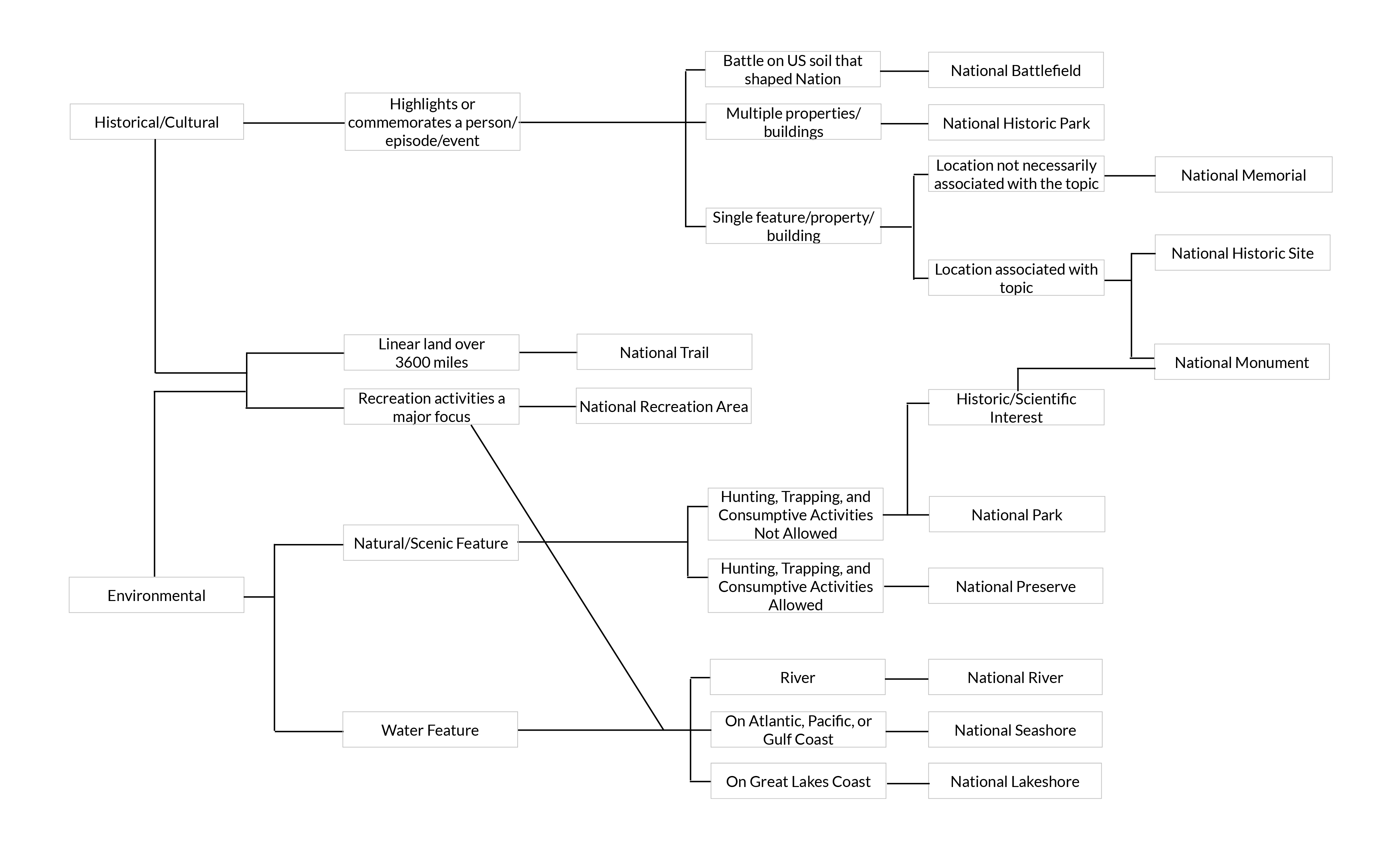
To see a full size version of the image click here.
In addition to the units captured in the image, there are two more units used by NPS:
- National Parkway: A motor roadway that parallels parkland. It is seen as a scenic drive along a protected corridor. A parkway often connects multiple sites.
- Other Designation: In some instances, a given location has a unique title or combination of titles.
The NPS partners with other organizations and government levels (e.g., state/local) to help with the “Affiliated areas”. These areas are not part of the NPS but help preserve other significant resources or history. Finally, during the life of a NPS location, the designations will shift based on restructuring, additional land/property inclusion, or park needs.
Source: NPS – Criteria for Parklands Brochure: http://parkplanning.nps.gov/files/Criteria%20for%20New%20Parklands.pdf
Source: Congressional Research Service: https://www.fas.org/sgp/crs/misc/R41816.pdf
Source: Wikipedia – NPS: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/National_Park_Service